Creating a Table
Overview
A Local Database consists of one or more tables which are created in the Local Database module.
![]()
A table must be well structured. Editing a table's properties, later on, results in the loss of data already inserted into the table.
To Create a Table
There are two ways to create a table:
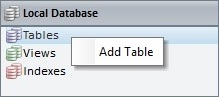
•Directly in the "Local Database" module.
Right-click the "Tables" section, within that module, and click "Add Table" in the resulting menu.
OR
•Click ![]() in whatever window it is available in (the properties window of most of the Local Database processes).
in whatever window it is available in (the properties window of most of the Local Database processes).
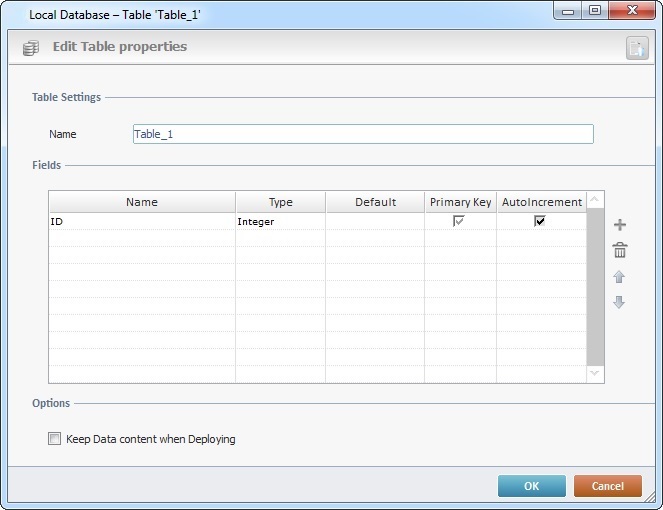
Whatever the path used, it opens a properties window which allows you to create/set up a table.
Step-by-step
1. In the "Table Settings" section, enter a name for the new table.
2. Fill in the "Fields" table:
Fields |
|
Name |
Enter the name of each required field. By default, you are provided with a field name suggestion ("ID") but it can be edited/replaced. |
Type |
Select the data type for the field from the drop-down list (Text, Integer, Real, Boolean, Date, Date + Time). |
Default |
If required, enter a default value for the field. |
Primary Key |
If you want a field to be a primary key, check the corresponding checkbox. |
AutoIncrement |
If you want the value of a primary key field to increment automatically, check the corresponding box. |
3. Use the icons to the right of the table to add (![]() ), delete (
), delete (![]() ) or move (
) or move (![]()
![]() ) the selected fields.
) the selected fields.
4. As an option, check the "Keep Data content when Deploying" option to ensure the sending of data along with the database structure to the device.
![]() Ensuring data delivery is not very useful at a business logic level because an application handles values that change over time (ex: item lists, product price lists, client lists, etc.) but it can make sense in a development context or, for instance, when defining a table containing an application's exception errors (values that do not change with time).
Ensuring data delivery is not very useful at a business logic level because an application handles values that change over time (ex: item lists, product price lists, client lists, etc.) but it can make sense in a development context or, for instance, when defining a table containing an application's exception errors (values that do not change with time).
5. Click ![]() to conclude.
to conclude.
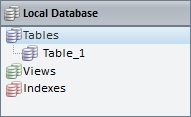
The new table is displayed in the "Tables" section of the "Local Database" module.