Recommendations on the Use of Speech Applications
Overview
When developing speech applications some best practices apply to the way the speech dialogs are constructed.
The same is valid for operators using a speech application.
Development Best Practices
Take these recommendations into account, as much as possible, when developing speech applications.
•Avoid using similar sounding words within the same active vocabulary, such as "lift" and "left".
•Avoid words that are too short, such as "up" or "skip" as well as words that are too long. Ideally, choose words two with 2 syllables.
Ex: In the case of an alphanumeric speech input, use NATO Alphabet (al-pha, bra-vo, char-lie, etc.).
•Avoid using the same word in different phrases within the same active vocabulary. For example, do NOT use "next" and "next page" to prevent them being mixed up.
•Keep the vocabulary word list as short as possible - too many options introduces confusion and insertion risk.
•Use the "Hint" feature (expected speech input value(s) for a given context) on a speech input when the context allows for it.
•Use a "Global Validation Word" for variable digit input (to prevent single digit confirmation).
•Advised maximum length of variable digit input is 6 digits. Ex: a word sequence with more than one word list should only allow for a total maximum of 6 units (not counting the focus word and the option of a global validation word).
•Build robust speech grammars sequences. Do not create a massive word list with all the necessary spoken words, group the spoken words by type or function into different word lists.
Ex: A speech input concerning time ("X hours" "X minutes) should have a speech grammar constructed with 2 word lists - one for the hours and one for the minutes.
Best Practices for Operators using Speech Applications
For an operator to use a speech application and establish a dialog, he must have a device equipped with a headset (microphone and speakers).
Example of a dialog:
1. The device prompts a command which the operator hears through the headset speakers.
2.The operator speaks a command via the microphone creating an audio sample.
3. The audio sample is processed internally and categorized into:
a. noise
b. the actual speech (speech input).
4. The speech input is put through speech recognition.
5. The application reacts to the accepted speech input.
The categorization of the audio sample relies on a calibration procedure (performed by the operator) - the calibration identifies the environment's noise level and sets the threshold level accordingly.
The calibration procedure should be performed in the working environment, usually, in the beginning of work or when there are significant background noise changes.
Calibration Procedure
The calibration procedure consists of two stages - the first one relates to the proper handling of the used hardware (device + headsets). The second stage refers to interacting with the software (the speech application itself).
The calibration procedure is performed by the operator and requires him to be at his workplace.
The developer can also perform a calibration within a test environment (using MCL-Simulator).
Step-by-step
1. Ensure that the headset is properly connected to the device that has the speech application installed.
2. Place the headset in your head and position its microphone:
a. The microphone must be about one finger's width away from your face, just below your lower lip and parallel to (and not in front of) your mouth.
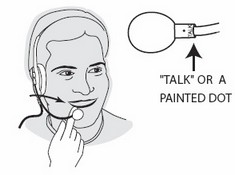
b. Make sure the microphone's "talk" or painted dot is facing you.
3. In the device, launch the application and check if the related speech icons are active (the microphone/speaker icons).
4. Pay attention to the screen and follow the prompted instructions. When repeating your instructions, speak normally (not too soft, not too loud).
The calibration starts with this window:

a. Remain silent during the viewing of this window.
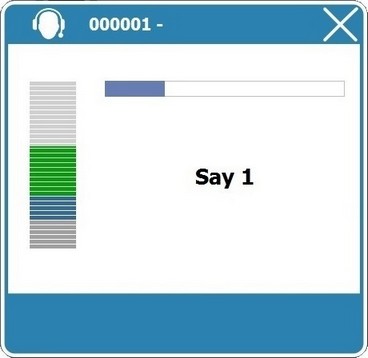
b. Say the intended word(s).

c. If you see this message, it means that the system did NOT understand you. Repeat the intended word(s) a bit louder.

Calibration was successful and you will proceed to the speech application itself.
To abort the calibration procedure (we do NOT recommend this), click ![]() (on the window's upper right corner).
(on the window's upper right corner).
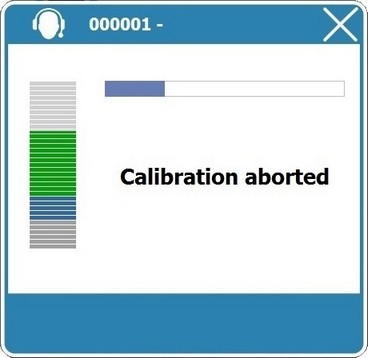
You will proceed to the speech application itself but the proper processing of the audio samples throughout the speech application session might be compromised.
Adaptation
Adaptation analyzes and stores the operator's user pronunciation characteristics (accent). It works with phonemes, meaning, it is NOT affected by the speech application's word lists.
Adaptation can be enabled for each operator in the MCL-Mobility Platform. This is a recommended process that should be performed by each operator handling a speech application because it is meant to improve overall recognition performance. Also, the operator only needs to perform it once and the resulting data will be available whenever he logs in to use the speech application.
Refer to the MCL-Mobility Platform User Guide for more information on Adaptation.
Speech Operator Management and Operator Login
Speech applications require speech operator management, and this is handled by the MCL-Mobility Platform. The MCL-Mobility Platform's "Operator Management" module is used to manage speech operators. For instance, by creating and, if necessary, customizing the speech profiles of the operators handling the speech application, you can optimize its results.
"Operator Login" is an action the operator needs to perform before the actual speech application starts. In order to execute this action, MCL-Technologies provides a "Login" application. This application is launched by the AppDesktop and is responsible for validating the operator ID, loading the operator profile and performing a Calibration (noise level identification).
After the "Operator Login" is performed, this event is also exposed in the MCL-Mobility Platform's "Operator Management" module (in the "Operators" page/"Operator Details" page).
Refer to the MCL-Mobility Platform User Guide for more information on Operators/Operator Login.