Working with the RFID Processes Group
Process Purpose
The RFID group of processes relates to wireless Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID). They enable a device to detect, read and decode information contained within RFID tags.
The use of RFID comprehends two functions:
Inventory - RFID tags are detected by the device operator with an RFID reader and there is an information exchange.
Single Tag - The information of the detected RFID tag is managed within the application (access, storage, reading, writing, etc.).
Depending on which function you use, you will use Synchronous or Asynchronous RFID processes:
Asynchronous processes - These commands are designed to enable/perform an Inventory (detection/communication between tag and reader device). They are executed on the background (ex: Enable/Disable, Start/Stop Reading).
Synchronous processes - Direct commands, to be used in the Single Tag function, related to the management of the information from tags (ex: Read, Write, Lock/Unlock, etc). The execution of these commands/processes is immediate, the application flow depends on it.
![]()
Make sure to use the “On RFID tag Read” event to complement your Inventory application.
See The On RFID Tag Read Event.
To Create a Simple Inventory Program
The creation of any RFID based program implies a few mandatory steps to ensure the necessary workflow:
1. Create an RFID profile with the required settings (see Creating an RFID Profile).
2. In a screen, enable the inventory operation (tag detection) with the "Enable/Disable" process. The enabling/disabling of a tag detection must always be explicit, so either use this "On Ready" event on the screen (hard start) OR create a button on that screen (soft start):
a. Soft Start ( button on screen)
You must add the "Start/Stop Reading" process to the button object. (This implies the adding of another button on screen to end the tag detection or the defining of a time out/number of tags read).
b. Hard Start (the target device's trigger)
The tag detection relies solely on the use of the device's trigger. There is no need to add a "Start/Stop Reading" process to the screen. Once the application reaches the intended screen (with the enabled tag detection), the device operator presses the trigger to perform the inventory and releases it to stop the operation.
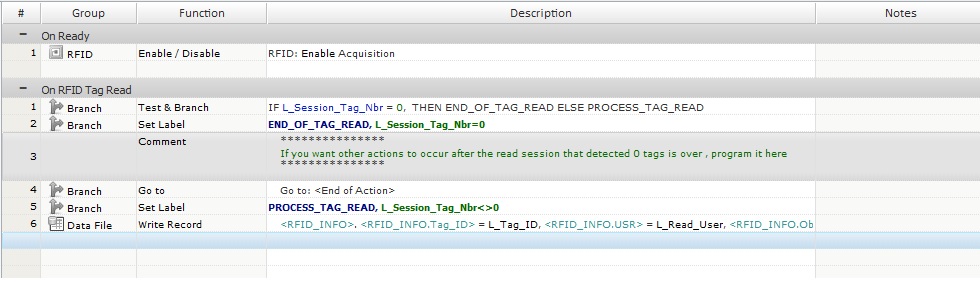
3. Use the "On RFID Tag Read" event on the same screen to capture the RFID tag readings asynchronously. This event allows you to set an RFID profile and to organize/store the tag's information. See The On RFID Tag Read Event. The "On RFID Tag Read" event is initiated for every new tag read.
4. To avoid a "0" tag detection display, use a Test & Branch process to redirect the application flow according to the number of tag detections
5. Disable the inventory operation with the "Enable/Disable" process. It must be explicit (ex: when leaving the screen where the Inventory takes place).
Example of a screen's "Actions" tab with a hard start.
This chapter covers the following topics:
----- Synchronous Commands |
----- Asynchronous Commands |
----- Other |