Local Procedures
Overview
A Local Procedure is a sequence of processes that acts within a program/global procedure and can only be called by that same program/global procedure.
It uses Local or Program variables to manipulate data.
To Add a Local Procedure to a Program
Step-by-step
1. Right-click the corresponding program or screen where the local procedure should be attached.
2. In the resulting menu, click the “Add Local Procedure” option.
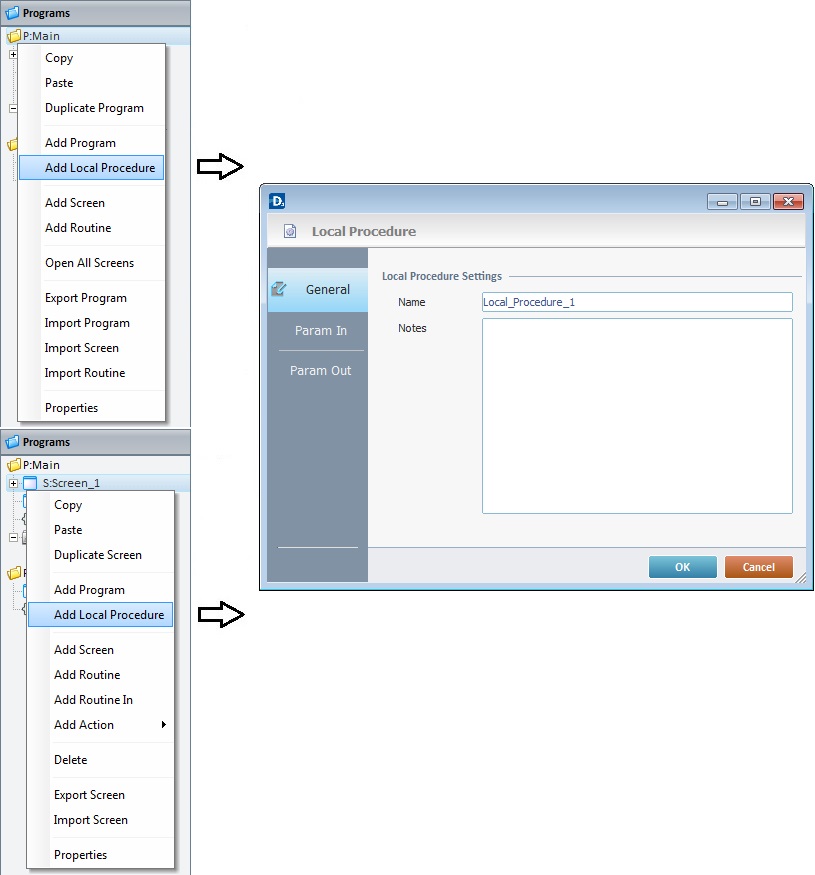
3. This opens a "properties" window.
In the "General" tab, enter a name to the newly created "Local Procedure" in the "Name" box. This name will be displayed in the tree view.
If necessary, add notes to the project by using the "Notes" box.
4. Go to the "Param In" tab.
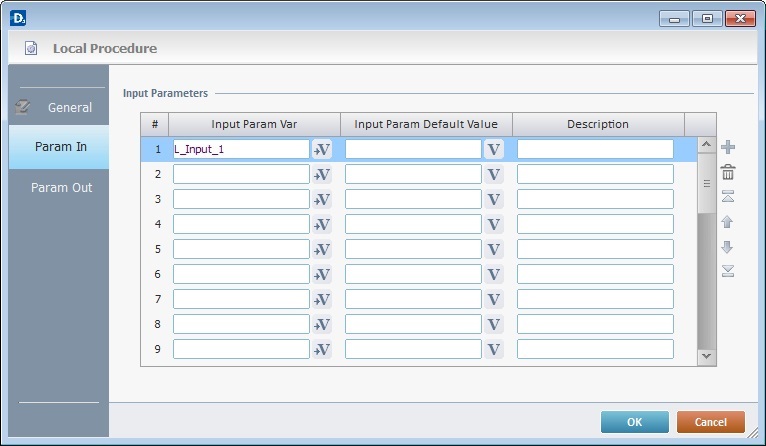
5. Define the input parameters for the local procedure in the columns:
"Input Param Var"
Define the local variable(s), within the local procedure, that receive data from outside, with the use of variables. See Working with the Variable Processes Group.
"Input Param Default Value"
Optionally, define the value(s)/variable(s) that are assigned to the "Input Param Var", in case the calling process does not map them.
"Description"
As an option, use the third column to add any relevant notes.
6. Go to the "Parameter Out" tab.
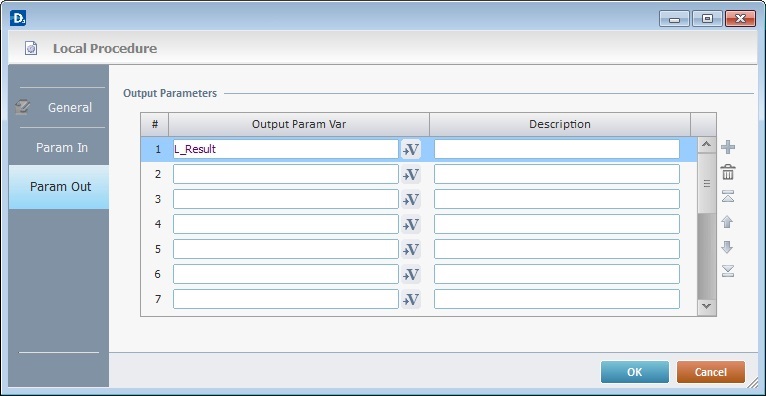
7. Define the output parameters for the local procedure.
"Output Param Var" – define the local variable(s) within the local procedure, that will return data to the program that called the local procedure.
"Description"
As an option, use the third column to add any relevant notes.
Use the editing icons to the right of the table to move the rows up and down and to delete or add more rows.
8. Click ![]() to finish adding a local procedure OR click
to finish adding a local procedure OR click ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
![]() To, actually, perform a local procedure's objective, it is necessary to use processes that will handle the input data.
To, actually, perform a local procedure's objective, it is necessary to use processes that will handle the input data.
This requires going back to the tree view.
9. Double-click the newly created local procedure name.
10. This opens a process window.
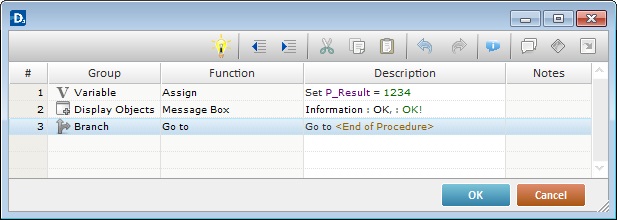
11. Add the required processes. See Adding Processes to Routines, "Routines In", Local Procedures or Global Event.
12. Always end the local procedure with a "Go to <End of Procedure>" process. This will return the program to the line, immediately below, that, initially, called for the local procedure.
13. Click ![]() to finish the adding of processes OR click
to finish the adding of processes OR click ![]() to abort the operation.
to abort the operation.
To Call a Local Procedure
This operation can be executed in a "process" window OR an "Actions" tab from the program that calls the local procedure.
Step-by-step
1. Add a “Branch Process – Call Local Proc”. See Working with Call Local Proc Process.
2. This opens the following window.
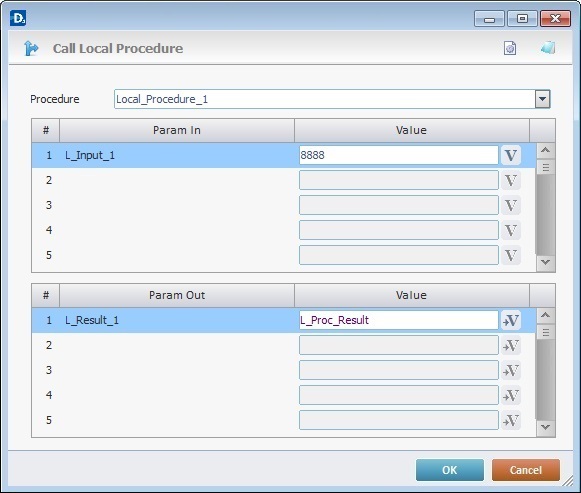
3. In the "Procedure" box, select the local procedure to be called.
4. The "Param In" automatically displays the parameters established in the "Properties" window ("Param In" tab).
Define the value(s)/variable(s) to be sent to the local procedure (mapping of the local procedure's input parameters) in the second column of the upper table.
5. The "Param Out", also, displays the parameters established in the "Properties" window ("Param Out" tab).
Define the variable(s) that return(s) data from the local procedure (mapping of the local procedure's output parameters) in the second column of the lower table.
![]() Clicking
Clicking ![]() (located on the window's upper right corner), enables the creation of a local procedure. See To add a Local Procedure to a Program.
(located on the window's upper right corner), enables the creation of a local procedure. See To add a Local Procedure to a Program.
6. Click ![]() to apply these choices and return to either the "process" window OR the "Actions" tab that initiated this operation.
to apply these choices and return to either the "process" window OR the "Actions" tab that initiated this operation.
7. Click ![]() in either the "process" window or the "Actions" tab to finish this operation.
in either the "process" window or the "Actions" tab to finish this operation.